- Information
- Symbol: ZFP252,RZF71
- MSU: LOC_Os12g39400
- RAPdb: Os12g0583700
- PSP score
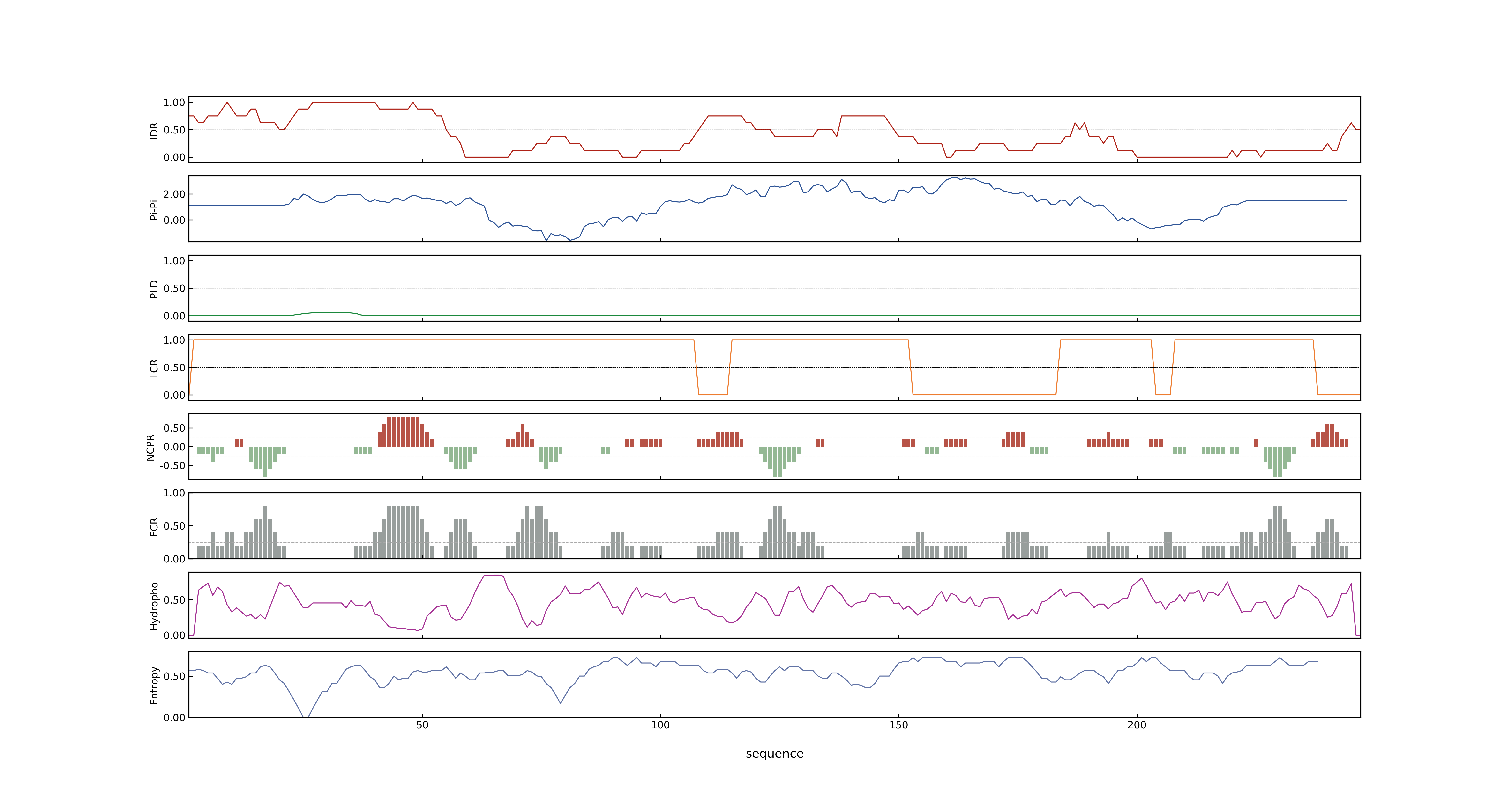
- LOC_Os12g39400.1: 0.5972
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os12g39400.1: 0
- pLDDT score
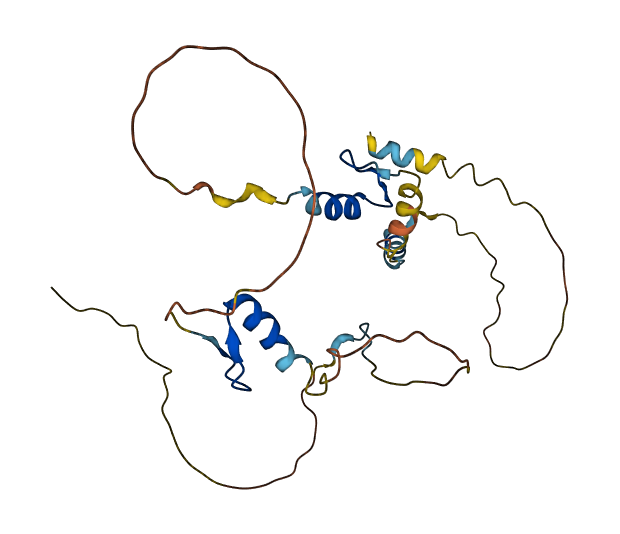
- 63.33
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os12g39400.1: 0.99935358
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- We previously identified a salt and drought stress-responsive TFIIIA-type zinc finger protein gene ZFP252 from rice
- We found that overexpression of ZFP252 in rice increased the amount of free proline and soluble sugars, elevated the expression of stress defense genes and enhanced rice tolerance to salt and drought stresses, as compared with ZFP252 antisense and non-transgenic plants
- Our findings suggest that ZFP252 plays an important role in rice response to salt and drought stresses and is useful in engineering crop plants with enhanced tolerance to salt and drought stresses
- Overexpression of a TFIIIA-type zinc finger protein gene ZFP252 enhances drought and salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- These results indicated that the RZF71 may play an important role in rice responses to salt and osmotic stresses as a transcription factor
- The semi-quantitative RT-PCR assay showed RZF71 was strongly induced by high-salinity and 20% PEG6000 treatments, but not regulated by low temperature and ABA (abscisic acid) treatments
- The expression profiling showed that RZF71 was constitutively expressed in roots, culms, leaves, and flowering spikes
- A rice zinc-finger protein gene, RZF71, encoding the C2H2-type zinc-finger transcription factor was isolated from rice
- Connection
Prev Next