- Information
- Symbol: eIF-1
- MSU: LOC_Os07g34589
- RAPdb: Os07g0529800
- PSP score
- LOC_Os07g34589.3: 0.0473
- LOC_Os07g34589.2: 0.0473
- LOC_Os07g34589.4: 0.0027
- LOC_Os07g34589.6: 0.0273
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os07g34589.3: 0
- LOC_Os07g34589.2: 0
- LOC_Os07g34589.4: 0
- LOC_Os07g34589.6: 0
- pLDDT score
- 76.71
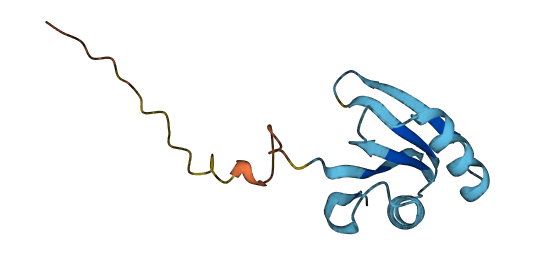
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os07g34589.2: 0.00933742
- LOC_Os07g34589.3: 0.00933742
- LOC_Os07g34589.4: 0.00079381
- LOC_Os07g34589.6: 0.00049998
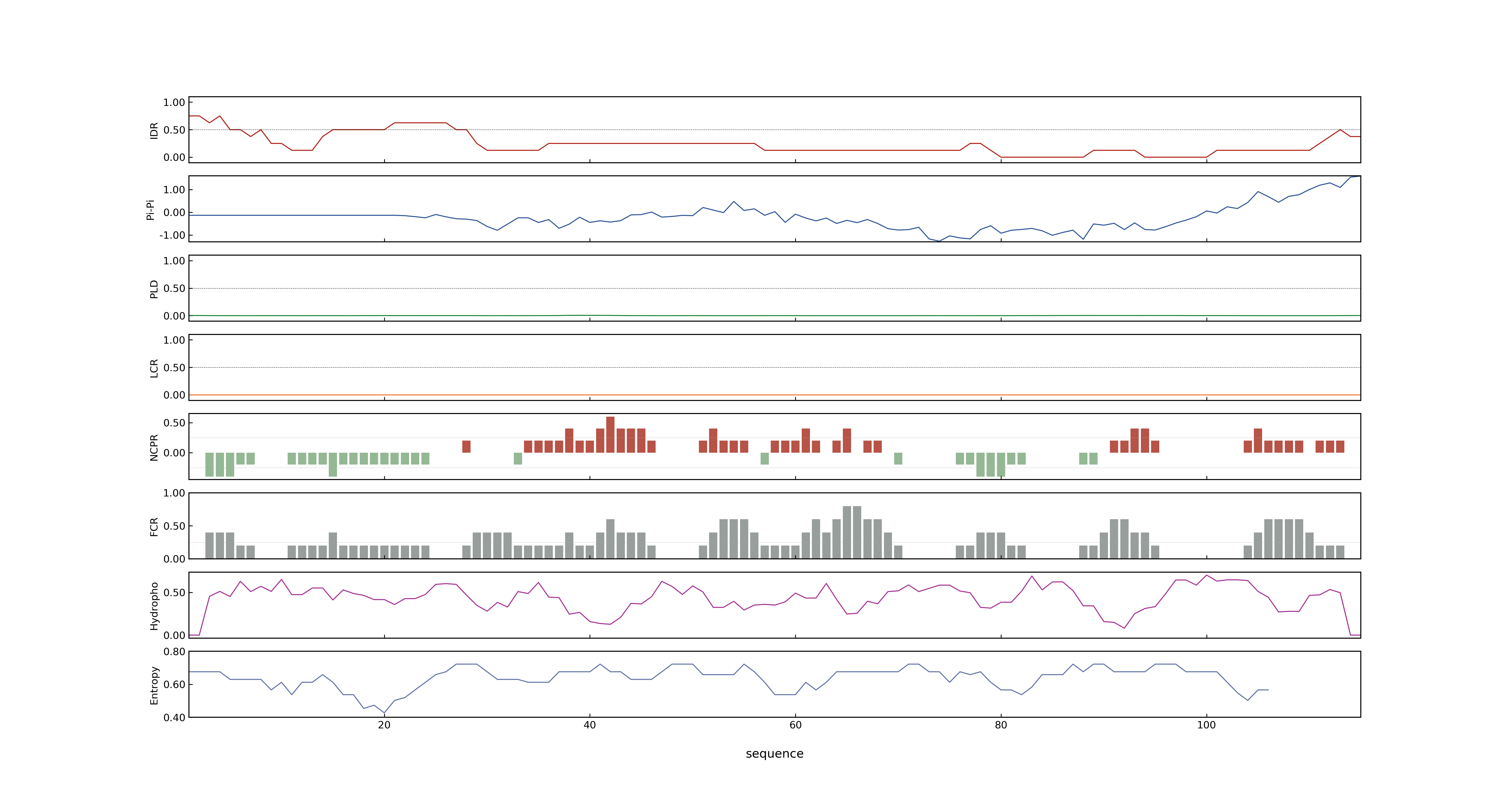
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- The SUI-homologous translation initiation factor eIF-1 is involved in regulation of ion homeostasis in rice, 2008, Plant Biol (Stuttg).
-
Genbank accession number
- Key message
- The eIF-1 over-expressing lines showed improved growth under salt stress that was correlated with maintenance of photosynthetic activity and reduced Na(+) and Cl(-) accumulation in leaves
- In a search for novel molecular mechanisms involved in salt acclimation, transcript analyses revealed increased expression of a SUI-homologous translation initiation factor eIF-1 in the salt-tolerant grass species Festuca rubra ssp
- To further examine the role of eIF-1 in salt tolerance, transgenic rice plants were generated that over-express this factor under the control of the CaMV-35S promoter
- Our data suggest that eIF-1 has a central function in salt-stress adaptation in rice by regulating ion accumulation and the intracellular redox status
- Upon analysis of the cell specificity of eIF-1 transcription by in situ polymerase chain reaction (PCR), predominant signals were detected in rice leaf mesophyll
- The SUI-homologous translation initiation factor eIF-1 is involved in regulation of ion homeostasis in rice
- Connection
Prev Next