- Information
- Symbol: spl5,SF3b3
- MSU: LOC_Os07g10390
- RAPdb: Os07g0203700
- PSP score
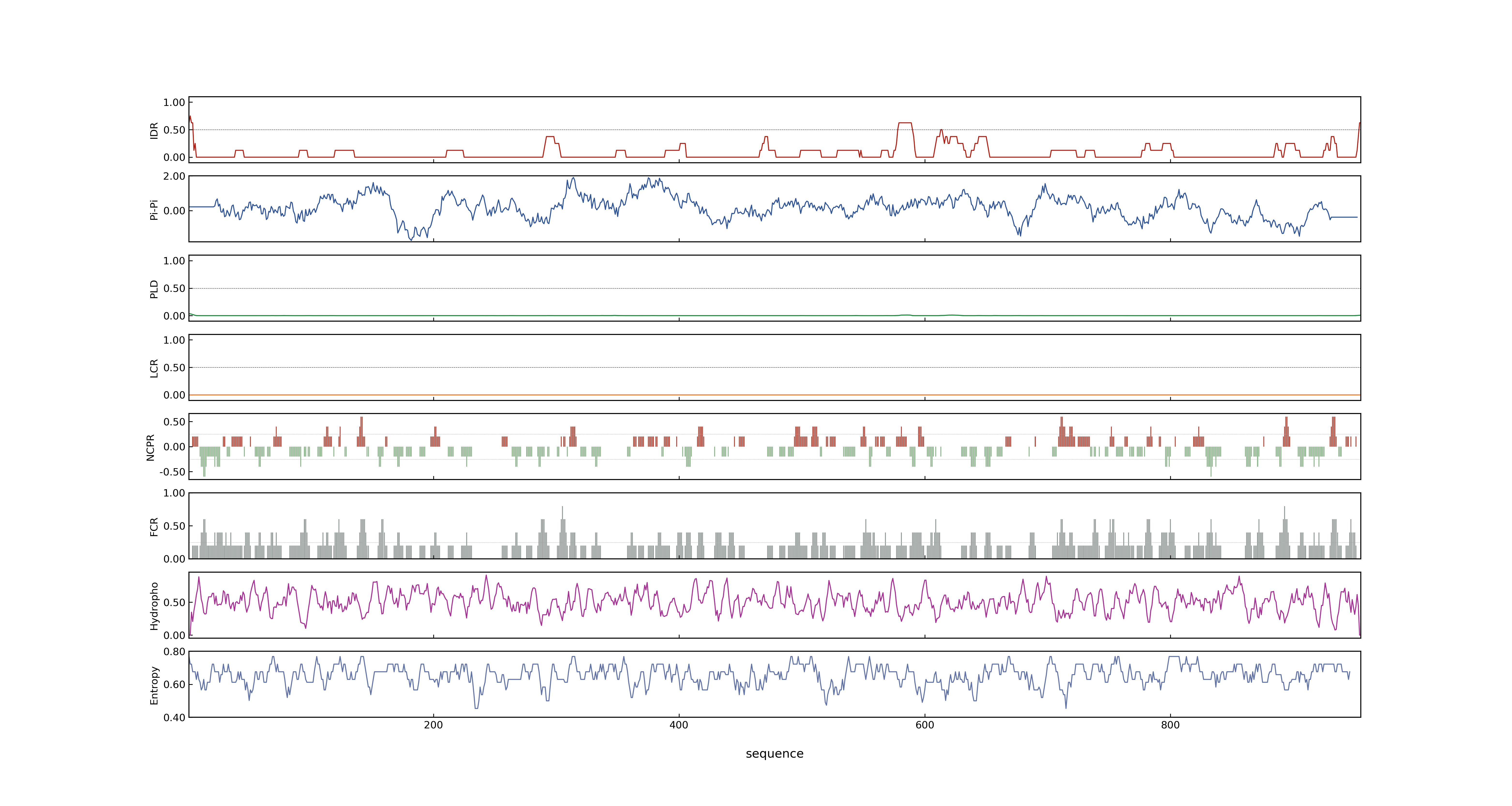
- LOC_Os07g10390.1: 0.2658
- PLAAC score
- LOC_Os07g10390.1: 0
- pLDDT score
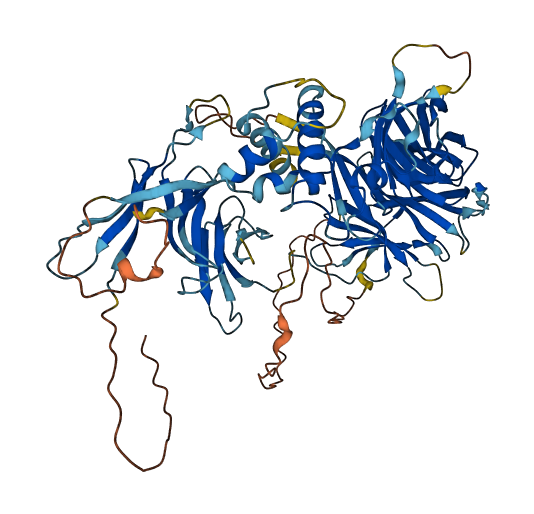
- 77.59
- Protein Structure from AlphaFold and UniProt
- MolPhase score
- LOC_Os07g10390.1: 0.69043964
- MolPhase Result
- Publication
- Genbank accession number
- Key message
- ) spotted leaf 5 (spl5) indicates that wild-type SPL5 negatively regulates cell death and resistance responses
- Bioinformatic analysis showed that SPL5 gene encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3 (SF3b3) and might be involved in splicing reactions of pre-mature RNAs participating in the regulation of cell death and resistance responses
- The data presented here clearly indicate that the SPL5 negatively regulates cell death and resistance responses via modulating RNA splicing in plants
- SPL5, a cell death and defense-related gene, encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3 (SF3b3) in rice
- Rice mutant, spl5 (spotted leaf 5), has spontaneous hypersensitive-like lesions on its leaves and shows enhanced resistance to pathogens, indicating that SPL5 plays a role in programmed cell death (PCD) and disease resistance
- Since the serotonin plays a critical role in inducing disease-resistance, the increased serotonin level may contribute, at least partly, to the disease resistance in spl5
- The SPL5 gene may act as a negative regulatory factor activating the serotonin metabolic pathway, and these results might provide a new insight into the spl5-induced defense response mechanisms in plants
- Interestingly, according to our microarray and real-time PCR assays, the expressions of a transcription factor OsWRKY14 and genes responsible for the biosynthesis of serotonin, anthranilate synthase (AS), indole-3-glycerolphosphate synthase (IGPS), tryptophan synthase (TS) and tryptophan decarboxylase (TDC) were significantly up-regulated in the spl5 mutant
- Transcriptome profiling of the spl5 mutant reveals that SPL5 has a negative role in the biosynthesis of serotonin for rice disease resistance.
- Connection
- OsWRKY14~OsWRKY33, spl5~SF3b3, Transcriptome profiling of the spl5 mutant reveals that SPL5 has a negative role in the biosynthesis of serotonin for rice disease resistance., Interestingly, according to our microarray and real-time PCR assays, the expressions of a transcription factor OsWRKY14 and genes responsible for the biosynthesis of serotonin, anthranilate synthase (AS), indole-3-glycerolphosphate synthase (IGPS), tryptophan synthase (TS) and tryptophan decarboxylase (TDC) were significantly up-regulated in the spl5 mutant
Prev Next